
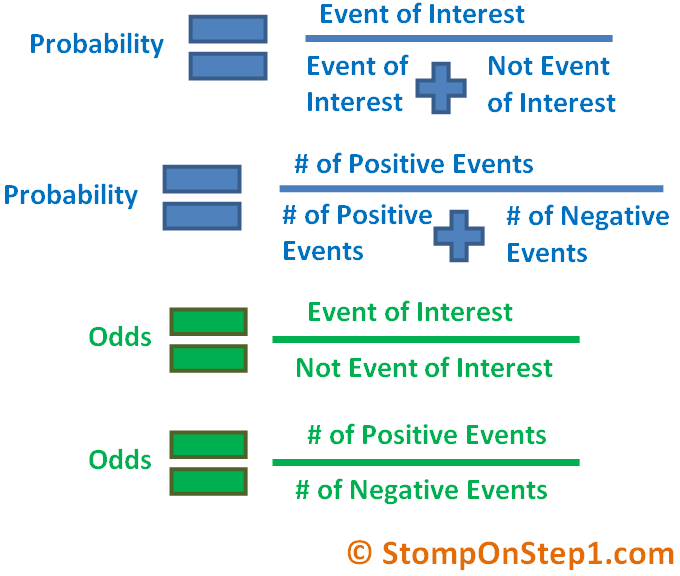
However, even if we are interested in knowing a specific risk scenario for a specific event, we can obtain this from a probabilistic assessment. We might adopt a deterministic approach to test an evacuation plan or mitigation strategy against a selected event. We would use a probabilistic approach to determine the likelihood of a number of different events. Whether we use a deterministic or probabilistic approach often depends on the type of question to be answered and disaster risk management decision to be made. The annual probability of exceeding a loss characterized by a 100-year return period is 1% - the inverse of the return period (1/100*100). The return period represents the annual probability of having a loss of this size every year. Likewise, it does not mean that if the loss occurred today that it would not recur for another 100 years. As the figure shows, the return period does not mean that the loss occurs every 100 years. Put simply, the 100-year return period loss (the magnitude 60 in our example) occurs, on average, once every 100 years. The time period between the nine losses ranges from sixty years to 200 years, meaning that on average losses of a magnitude of 60 were exceeded every 100 years - the return period of this loss. The figure shows a record 1000 years of losses of different sizes (magnitudes) - nine events exceeded a loss of '60' over that period. What do we mean by return period? Take the following example adapted from the UNISDR Global Assessment Report 2015: In the context of disaster risk, probability refers to the frequency of occurrence or the return period of losses associated with hazardous events. This method assesses the likelihood of an event(s) and it contains the idea of uncertainty because it incorporates the concept of randomness. Probabilistic risk is the chance of something adverse occurring. In order to address this short-fall, we have to adopt a probabilistic approach. Consequently, deterministic scenario planning may actually be underestimate the potential risk.
Risk probability method full#
There are a number of problems with a deterministic approach, including the fact that it does not consider the full range of possible outcomes, and does not quantify the likelihood of each of these outcomes. running multiple scenarios at different probabilities of occurrence) can be used to generate a deterministic scenario typical scenarios might include: For example, probabilistic modelling (i.e. There is overlap in deterministic and probabilistic modelling.
The deterministic approach typically models scenarios, where the input values are known and the outcome is observed. In contrast, a deterministic model treats the probability of an event as finite.

Probabilistic models therefore "complete" historical records by reproducing the physics of the phenomena and recreating the intensity of a large number of synthetic events. As a result, these risk assessments resolve the problem posed by the limits of historical data. Probabilistic risk assessment simulates those future disasters which, based on scientific evidence, are likely to occur. While historical losses can explain the past, they do not necessarily provide a good guide to the future most disasters that could happen have not happened yet. OECD, 2012 What is the difference between deterministic and probabilistic risk? Probabilistic assessments are characterized by inherent uncertainties, partly related to the natural randomness of hazards, and partly because of our incomplete understanding and measurement of the hazards, exposure and vulnerability under consideration. Deterministic risk considers the impact of a single risk scenario, whereas probabilistic risk considers all possible scenarios, their likelihood and associated impacts.ĭeterministic approaches are used to assess disaster impacts of a given hazard scenario, whereas probabilistic methods are used to obtain more refined estimates of hazard frequencies and damages.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
